Definition of the GDPR
The GDPR, or General Data Protection Regulation, is a European Union regulation aimed at protecting individuals' personal data. It came into effect on May 25, 2018 and establishes strict rules for the collection, processing, and storage of data, as well as penalties for non-compliance. Its goal is to harmonize data protection practices across the EU and ensure the confidentiality and security of personal information.
The full text of the regulation can be downloaded from this link.
What is the objective of the GDPR?
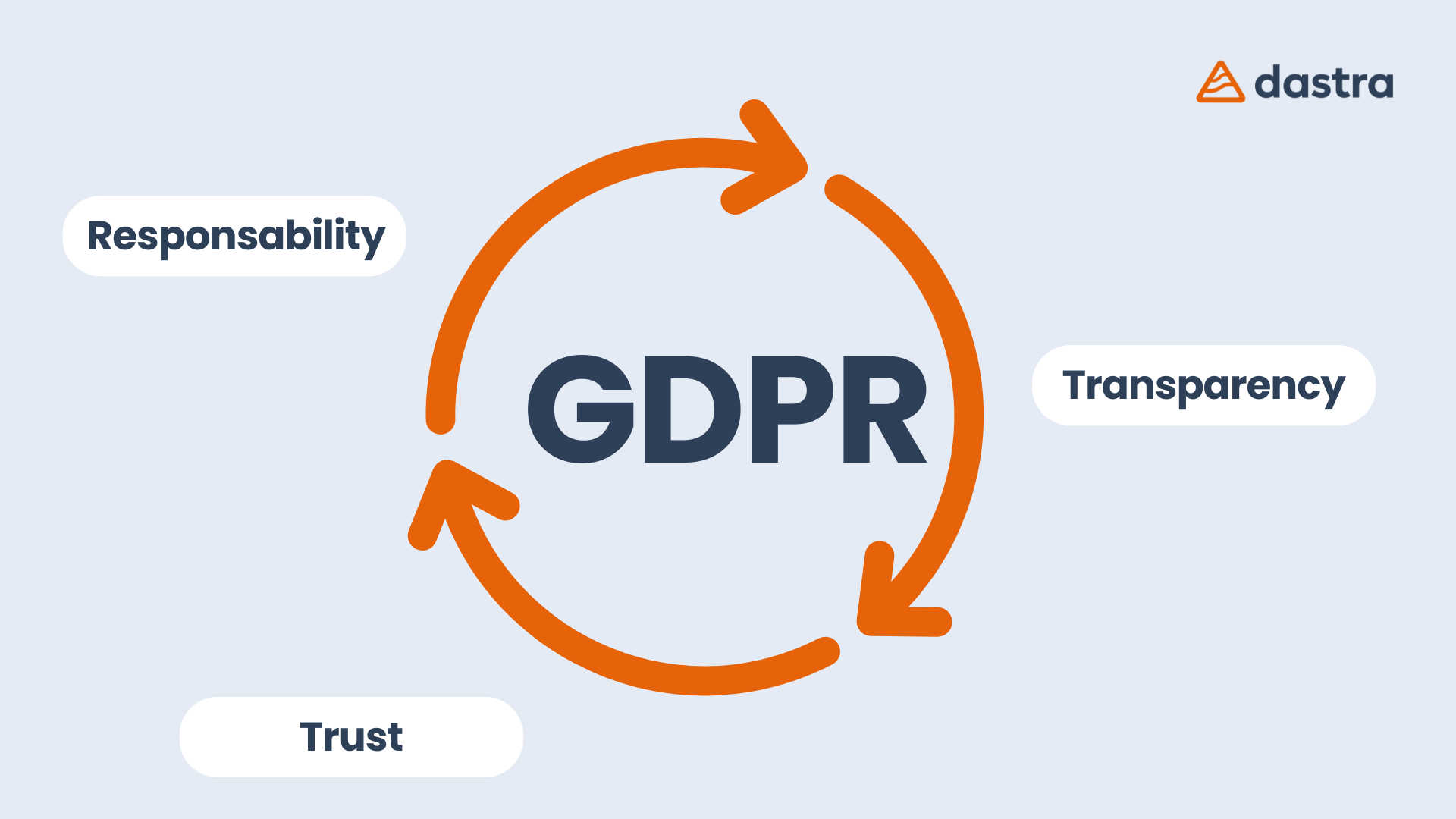
The GDPR aims to give individuals more control over their personal data and to instill greater trust in how businesses and institutions handle this data. Key principles at the heart of the GDPR are designed to protect privacy and individuals' rights.
3 Objectives:
- Enhancing individuals' rights
- Encouraging responsibility for data-handling stakeholders
- Increasing the legitimacy of regulation through closer collaboration between data protection authorities
Who is affected by the GDPR?
The GDPR applies to any organization, regardless of size or geographic location:
- located within the European Economic Area (EU + Liechtenstein + Norway + Iceland). or
- collecting, processing, or storing personal data of individuals located within the European Economic Area (EU + Liechtenstein + Norway + Iceland).
This includes:
- companies
- non-profit organizations
- governmental institutions
- marketing agencies
- online service providers
- and any other entity processing personal data in the course of their commercial activities or interactions with individuals from the EU.
- Additionally, the GDPR also applies to processors and service providers handling personal data on behalf of an organization subject to the regulation.
In summary, any entity that handles personal data of EU citizens must comply with the provisions of the GDPR.
Legal bases, including consent
One of the key aspects of the GDPR is the requirement for a legal basis to process data, which includes consent. In certain cases, organizations must obtain clear and specific consent from individuals before collecting and processing their personal data. This consent must be freely given, informed, and revocable at any time by the individual. Six legal bases allow for the processing of personal data:
- consent
- legitimate interests
- vital interests
- public interest
- legal obligation
- contract
Rights of individuals
The regulation also grants individuals a number of rights regarding their personal data. These include the right of access, allowing individuals to know what data is held about them, and the right to data portability, enabling them to easily transfer their data from one service to another.
Responsibility
Another key provision of the GDPR is the principle of organizational responsibility and transparency. Companies must be able to demonstrate their compliance with the GDPR by implementing data protection measures and maintaining detailed records of their data processing activities.
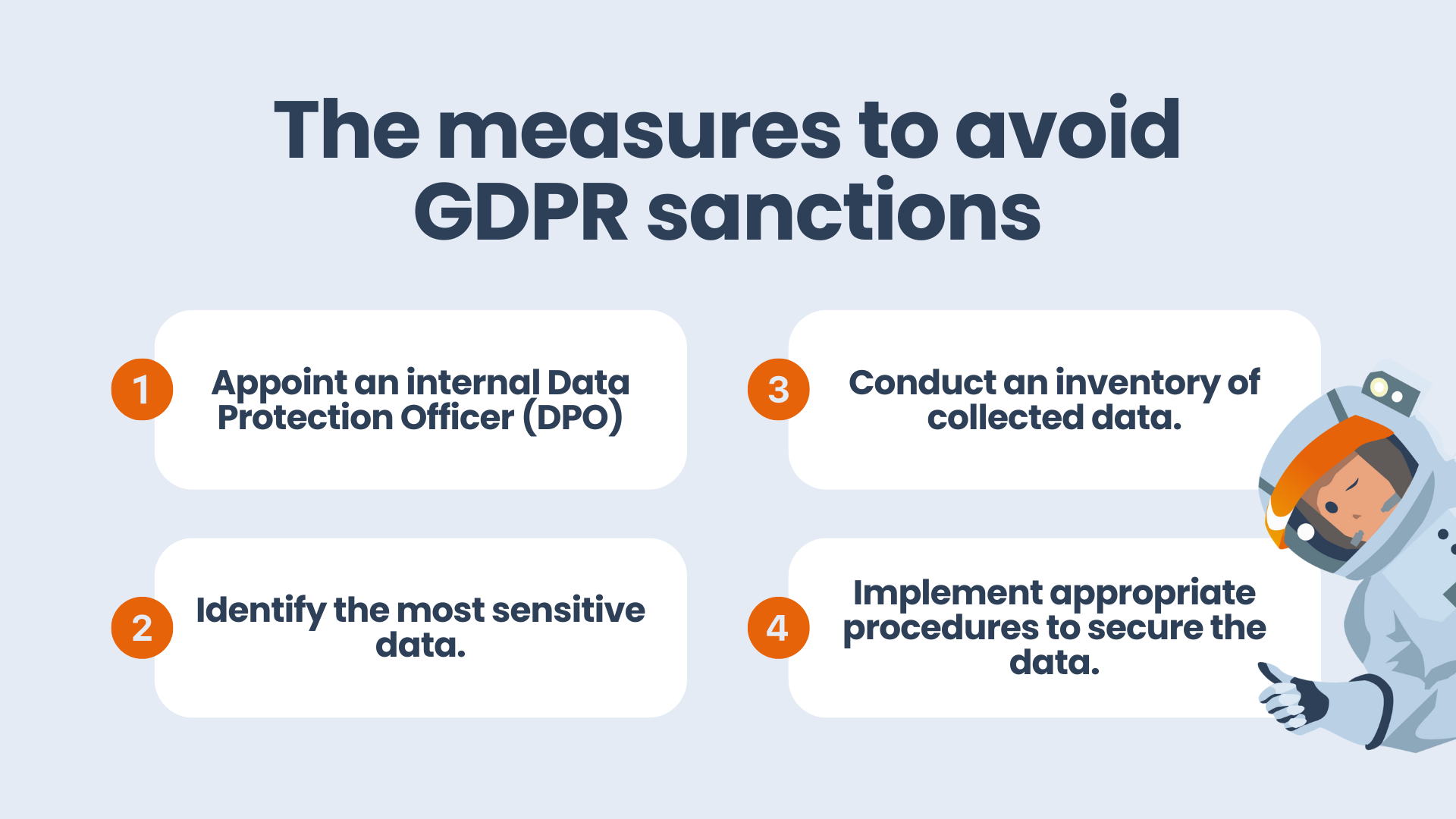
GDPR sanctions
The GDPR also introduces severe penalties for non-compliance. Data protection authorities are empowered to impose fines of up to 4% of a company's annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
The GDPR aims to create an environment where individuals have control over their own data and organizations handle this data in a responsible and ethical manner.
While its implementation may pose a challenge for many businesses, the GDPR represents a significant step towards better privacy protection and individual rights in the digital age.
Dastra GDPR Software
Want to comply with the GDPR? Dastra software offers many features to help you meet data protection standards. To find out more, contact one of our experts !
